The OSHA Alliance Program is a cooperative effort to leverage resources related to safety initiatives, communication, and training. OSHA Alliance includes ‘unions, consulates, trade or professional organizations, faith- and community-based organizations, businesses, and educational institutions’ that promote work safety and support OSHA’s strategic goals. Alliance members must be committed to working closely with OSHA and establishing teams or individual workers to facilitate the cause, while maintaining and growing knowledge and a safe work environment. In addition to internal safety benefits, Alliance members are able to maintain progressive dialogue with OSHA and other champions of work safety. To learn more, contact your OSHA Regional Office.
OSHA Ladder Fall Prevention Campaign
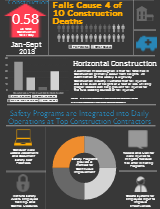
One of OSHA’s ongoing strategic goals is to mitigate risks and increase knowledge regarding falls from ladders. Fall incidents are the leading cause of deaths in construction and present a wide range of potential work hazards. Considering the variability of material, application, and objective for ladders and stairs, it is not surprising that OSHA produces a significant amount of standards and guidelines for fall protection safety. In addition to OSHA’s ongoing Ladder Fall Prevention Campaign, requirements and resources that support this cause are provided by specialized organizations such as ANSI and MSHA (Mining Ladder Safety).
OSHA Alliance Solution: Fixed Ladders or Stairways
The OSHA Alliance Program has produced a summary solution document as a resource for preventing falls from ladders in construction work environments. This Construction Safety Design Solution recommends specifying fixed ladders or stairways early on to eliminate the hazards and risks associated with portable ladders and to ensure proper ladder or stairway specifications for access to upper levels. The document also provides links to applicable OSHA regulations and ANSI standards for detailed information. Visit OSHA Alliance member Prevention through Design for more work safety resources.
Custom Fixed Ladder or Stairway Design
Innovative Access Solutions has been producing fixed ladders and stairways for construction, manufacturing, maritime, energy, and other industries for many years.
Information about how IAS can help support your work safety initiatives is available at IAScustom.com, or click the above images to browse our custom design gallery.



![Slip & Fall Injuries in Truck Transportation [Infographic]](http://snblog.preview.yellowberri.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Slips-and-Falls-Trucking-SQUARE_Mar2013.png)